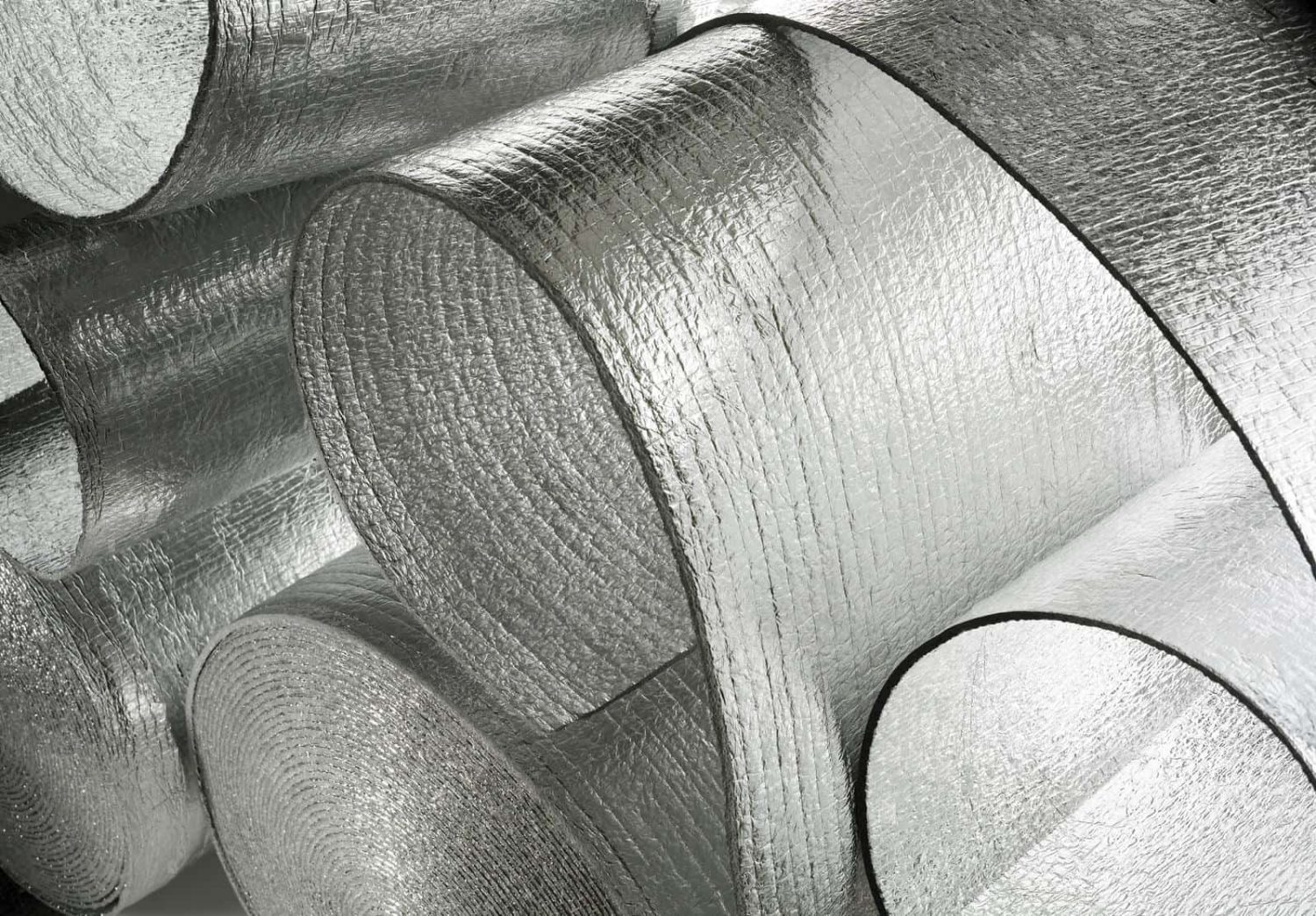
The production of laminated insulation materials has been an integral part of the scientific and industrial world for decades. Through advances in technology, engineers and scientists have developed a range of highly efficient materials that provide superior protection from heat or cold.
This article will explore the science behind laminated insulation material production, looking at how these materials are made and their applications in construction, manufacturing, and other industries. It will also discuss why they are so effective at insulating against temperature extremes.
Raw Materials Used in Laminated Insulation Material Production
Raw materials are the building blocks used in the production of laminated insulation material. Depending on where it is being produced, these raw materials may vary. For example, products that use glass fibers often require sand or soda ash to be melted down and spun into a fine yarn-like filament. This process requires extreme temperatures which can be achieved with natural gas burners or electric arc furnaces.
Other types of insulation materials such as polyester-based materials will not require such drastic conditions and instead involve more conventional processes like cutting and welding plastic sheets together using high-heat machines or adhesives. Additionally, nonwoven fabrics like felt may also be needed for some applications depending on the desired performance characteristics of the finished product.
Once all of these components are properly sourced and prepared, they can then move onward to the assembly where they will be cut into pieces and fused according to precise specifications before going through quality control tests before shipping out for customer use.
Steps of the Manufacturing Process

Source: fabricarchitecturemag.com
The manufacturing process of laminated insulation material production is a complex but rewarding one. It starts with the selection and preparation of raw materials, including fiberglass or mineral wool, which will form the core insulation layer. These materials are then combined with adhesive resins to create an insulation board that is both fire-resistant and durable.
After this initial step, it’s time for lamination, where these boards are coated in plastic film or foil to further improve their thermal efficiency and lifespan. The final steps involve cutting the boards into specified sizes and shapes as well as testing them for quality control purposes before they can be shipped off to customers. All in all, it takes careful planning and precision throughout each stage of production to ensure that the end product meets its desired specifications.
Benefits of Laminated Insulation Materials
The benefits of using laminated insulation materials for production are numerous. From improved energy efficiency to increased fire safety, laminated insulation material provides the perfect combination of durability and performance. In terms of energy efficiency, laminated insulation material helps industries reduce costs by reducing air infiltration through walls and windows. Furthermore, it also adds a layer of protection that traditional materials cant provide.
In terms of fire safety, laminated insulation material offers superior protection from flames due to its special construction process that includes multiple layers bonded together with adhesive. This makes the product resistant to both high temperatures and flame retardants allowing industries to create a safer working environment with minimal impact on productivity levels. Moreover, this type of insulation is lightweight yet strong making it suitable for a variety of applications in different industrial settings where weight restrictions may apply such as aircraft or other vehicle manufacturing operations.
Additionally, it also has excellent noise reduction properties which makes it ideal for use in areas where soundproofing is needed like recording studios or music venues. All these factors make laminated insulation materials an ideal choice for any industry looking to improve their operational efficiency while ensuring maximum safety standards are met at all times – ultimately helping them achieve long-term success and profitability goals without compromising on quality assurance or environmental responsibility measures.
Chemical Properties and Physical Characteristics of Laminated Insulation Materials
Laminated insulation material production is heavily reliant on an understanding of its chemical and physical characteristics. By knowing the chemical makeup of materials, manufacturers can create a product that will provide maximum protection from heat and cold. For instance, laminated insulation materials often contain cellulose fibers which are strong yet lightweight. Additionally, these fibers act as insulators to retain warmth or cool air depending on the environment. The physical properties of any given laminate insulation material are also important aspects to consider when it comes to making a quality product.
They need to be thick enough to provide adequate coverage without being too heavy for their intended purpose. Furthermore, they must be able to withstand extreme temperatures while still staying flexible so as not to damage other components around them. Different additives such as glass fibers or aluminum foil may also play a role in how well the material performs over time due to their reflective properties aiding in thermal management and thus improving efficiency levels overall.
In short, there’s much more than meets the eye about producing reliable laminated insulation materials – careful consideration of both its chemical composition and physical attributes are key factors in making sure you get an effective product that lasts for years down the line!




